Bonus Tax Calculator USA
Tax Breakdown
Note: This calculator provides estimates based on current IRS rules for supplemental wages. Actual tax withholding may vary based on your specific circumstances. For official tax advice, please consult a tax professional.
Explore Our Free Tax Calculators and Tools
Bonus Tax Calculator USA
A bonus tax calculator is an online tool that estimates the amount of federal and state taxes withheld from employee bonuses. Employers often award bonuses for performance, retention, or signing incentives, but unlike regular salary, these payments are taxed differently under IRS rules. Using a bonus after tax calculator or signing bonus tax calculator helps employees determine their net take-home bonus by applying the percentage or aggregate tax method. This guide explains how bonuses are taxed in the United States and shows how to calculate your after-tax bonus quickly and accurately.
How Are Bonuses Taxed in the U.S.?
Since bonuses are taxed as Supplemental Income in the United States by IRS, they are liable to the same taxes as your regular income, including Social Security and Medicare as well as federal, state, and local income taxes. Various techniques are employed by employers to withhold taxes from bonuses. A flat rate, typically 22% for federal taxes, is withheld in the percentage method. Alternatively, you can use the aggregate approach, which combines the bonus with your normal pay and uses your total income to determine your taxes. Tax withholding may occasionally be higher as a result of this than it would be from your normal pay cheques. A bonus tax calculator is a useful tool for estimating your take-home pay so that you may make appropriate plans.
1. Percentage Method
This is the most common method used for one-time bonuses like a signing bonus or holiday bonus. The IRS applies a flat federal tax rate of 22% (as of 2025) on your bonus.
Example:
-
- Bonus amount: $5,000
-
- Federal tax withheld: 22% of $5,000 = $1,100
-
- Take-home bonus (before other deductions): $3,900
2. Aggregate Method
In this method, your bonus is added to your most recent paycheck, and the total amount is taxed as one larger paycheck. This can result in higher withholding if you’re pushed into a higher tax bracket temporarily.
Note: In both cases, state taxes, Medicare (1.45%), and Social Security (6.2%) may also apply depending on your income.

Understanding Your After-Tax Bonus
To know what you’ll actually receive, you must consider:
-
- Federal tax (22% if flat method)
-
- State income tax (varies by state)
-
- FICA (Social Security and Medicare)
-
- Local/city taxes (if applicable)
Rather than manually calculating, you can use an after tax bonus calculator to get a quick and accurate estimate. Examining real-world examples that illustrate the distinction between pre-tax and post-tax amounts is necessary to comprehend your after-tax bonus. For example, if a bonus of $5,000 is taxed at a federal rate of 22%, \$1,100 will be withheld for federal taxes. However, because different states have varying tax rates, the total amount you receive may differ depending on your state.
Why Use a Bonus Tax Calculator?
In order to rapidly estimate your take-home bonus and prevent unpleasant surprises on payday, a bonus tax calculator is necessary. A comprehensive picture of your net income after all deductions makes it perfect for tax preparation and job offer negotiations. A bonus after taxes calculator helps you:
-
- Save time
-
- Avoid guesswork
-
- Make smarter financial decisions
-
- Understand how different states affect your take-home pay
Try Our Free Bonus Tax Calculator
Use a bonus tax calculator to see how much your take-home bonus will be. To obtain your anticipated take-home pay instantly, enter your bonus amount and choose your state. Our easy-to-use bonus tax calculator allows you to:
-
- Enter your bonus amount
-
- Select your state
-
- Instantly calculate your after-tax bonus
It factors in federal, state, and FICA taxes to give you an accurate estimate of what you’ll take home.
- Instantly calculate your after-tax bonus
Signing Bonus Tax Calculator: How It Works

Signing bonuses are typically taxed just like other bonuses. Whether you’re starting a new job in tech, finance, or healthcare, your signing bonus will likely be subject to the flat 22% federal tax rate, plus state and other applicable taxes.
Using a signing bonus tax calculator, you can:
-
- Determine your actual post-tax earnings from your offer
-
- Plan for future deductions or estimated tax payments
-
- Evaluate whether to negotiate for a higher gross bonus
Real-Life Example: Calculating a $10,000 Bonus
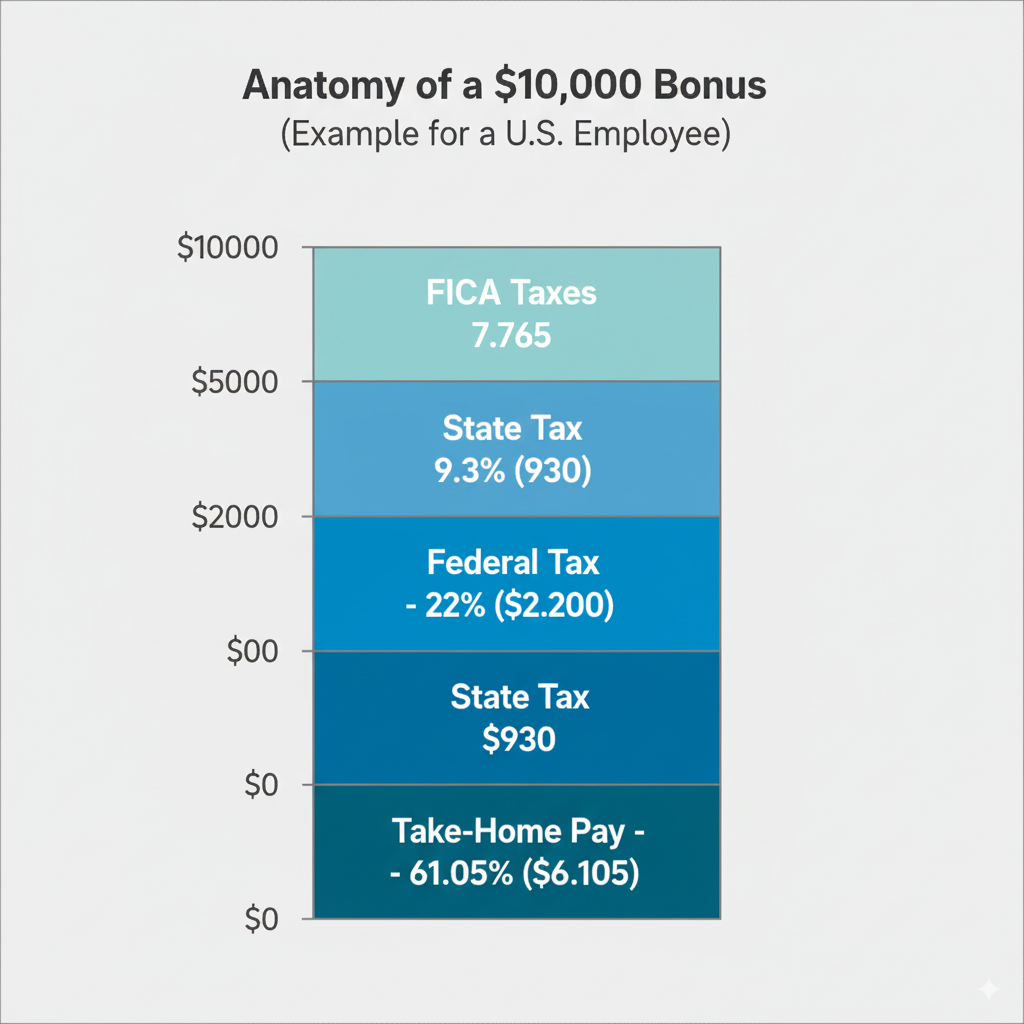
Let’s break it down for someone in California:
-
- Bonus: $10,000
-
- Federal tax (22%): $2,200
-
- State tax (CA ~9.3%): $930
-
- FICA taxes (~7.65%): $765
Total taxes: $3,895
Take-home bonus: $6,105
Note: Exact state rates vary; this is an estimate.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why is my bonus taxed more than my salary?
Because the IRS treats bonuses as supplemental income, they are often withheld at a flat 22% rate, which can be higher than your usual withholding.
2. Can I reduce the tax on my bonus?
You can’t avoid the tax, but deferring to a retirement plan (like a 401(k)) may help reduce taxable income overall.
3. Is the 22% tax on bonuses final?
No. It’s just withholding. Your actual tax owed is calculated when you file your annual tax return, and you may receive a refund or owe more based on your total income.
4. Are signing bonuses taxed the same way?
Yes, signing bonuses are also considered supplemental income and taxed using the same method as regular bonuses.
Conclusion
Bonuses are a great reward, but taxes can take a significant bite out of your windfall. By understanding how bonuses are taxed and using a reliable bonus tax calculator, you can plan more effectively and avoid surprises. Whether it’s a performance incentive or a signing bonus, knowing your after-tax bonus helps you make informed financial decisions. Finally, in order to properly manage their finances, U.S. employees must be aware of how bonuses are taxed. As supplemental income, bonuses are taxable at the federal, state, and municipal levels. They are sometimes withheld through procedures that result in higher tax rates than those of ordinary earnings. This can occasionally come as a shock to workers who were hoping for a higher net bonus. Using a bonus after-tax calculator is strongly suggested to precisely manage your money and prevent any financial surprises. These calculators account for all relevant taxes to give you a precise estimate of your take-home bonus.

Disclaimer: The tools and content on USATaxCalculator.com are for informational purposes only and do not constitute tax or financial advice. Our calculators provide basic estimates and may not reflect the exact tax results.
We recommend consulting a certified tax professional or the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) for accurate guidance. USATaxCalculator.com is not responsible for any decisions made based on the information provided.